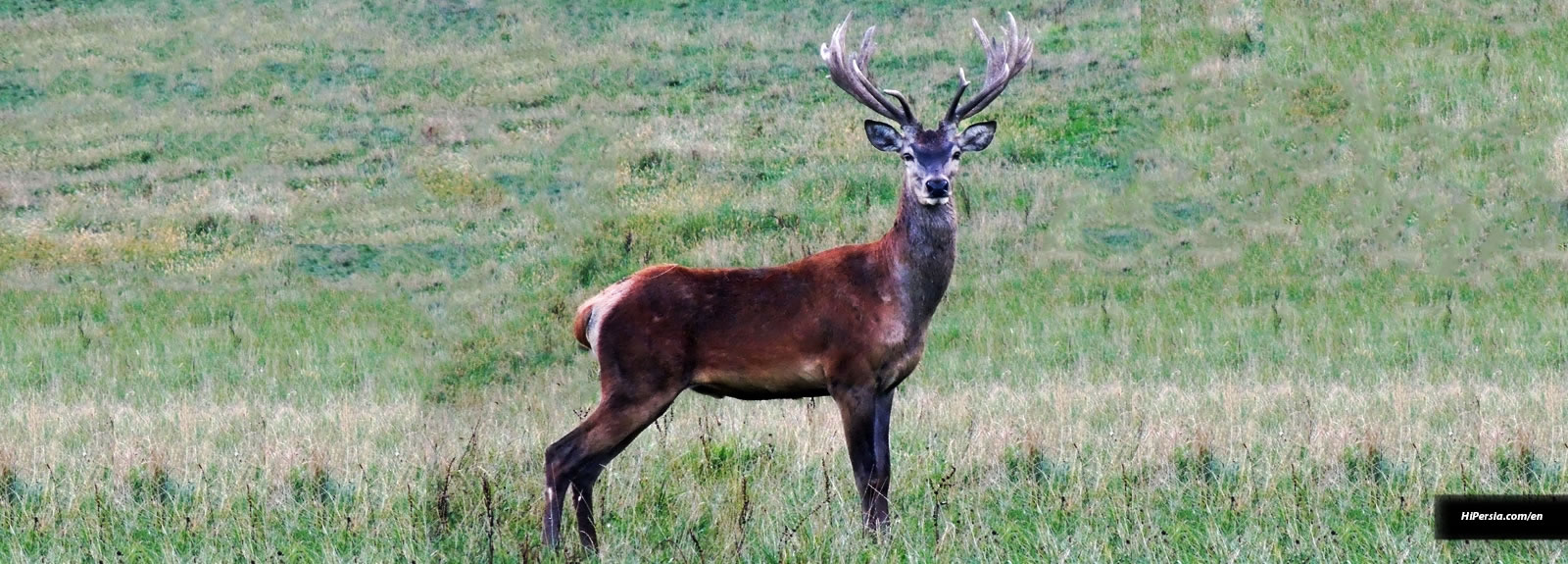




Persian fallow deer have golden skin and white spots. It is one of the most beautiful species of deer in the world. Because the animal first reported in western Iran, it named Persian fallow deer.
The Persian fallow deer have previously been widely distributed from Lorestan, Kermanshah, Khuzestan, Iraq, to the southeastern Mediterranean and North African regions. Researchers thought that deer had become extinct in Iran in 1955, but in the same year, the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) released a report that the number of fallow deer had been seen in the Dez and Karkheh districts of Khuzestan province.
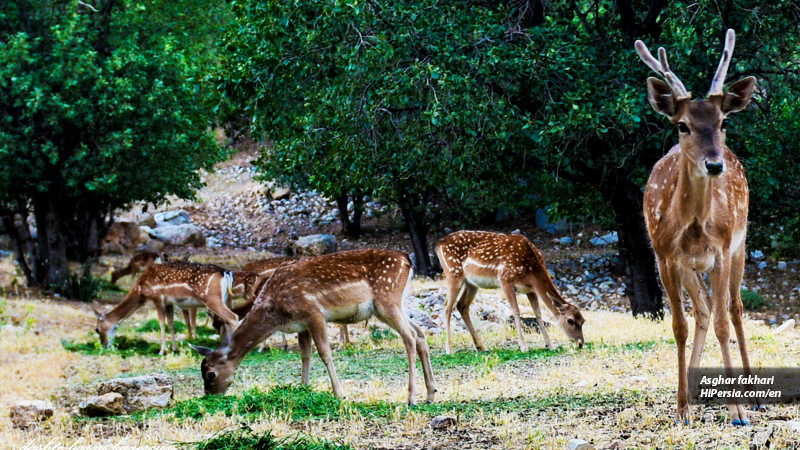

These kinds of deer start their activity at night. They are vegetarian and ruminant. These deer have golden skin with white dots. The Persian fallow deer have a relatively strong sense of smell and sight. These deer live socially, but the older males make a separate group for themselves. Only during mating, males move to females. Their food is forage and fruit. Mating of this type of deer is in early autumn. Females can mate more than once a year, but usually become pregnant during the first period. During pregnancy, it is eight months and one to two babies. The fawns are about three to four kg and are fed up breastfeeding for nine months of age. The life span of deer in natural conditions is about 20 years.

The Iranian Hunting Center put one Persian fallow deer in the Zoo Berlin in the year 1343, where another fallow deer was kept, provided that their lambs were divided between Iran and the Zoo Berlin. In the year 1351, five females and two male deer were transferred from Germany to the Dasht-e-Naz protected area in Sari. Subsequently, five wild fallow deer again were taken from the Karkheh area. Then transferred to the Dasht-e-Naz protected area of Sari, and the number of deer increased gradually. Three deer were transferred to Ashk Island in 1356. There are currently about 300 fallow deer on the Ashk Island.





“Oh! Squander not this breath that Heaven hath lent thee, Nor make too sure another breath to borrow!’” Khayam